- Home
- Science
- Science News
- James Webb Telescope Uncovers the Turbulent Birth of the First Galaxies
James Webb Telescope Uncovers the Turbulent Birth of the First Galaxies
The James Webb Space Telescope found that galaxies formed within 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang were turbulent and clumpy. Studying over 250 young systems, scientists saw chaotic gas flows and intense starbursts that later cooled, transforming these early galaxies into today’s stable spirals.
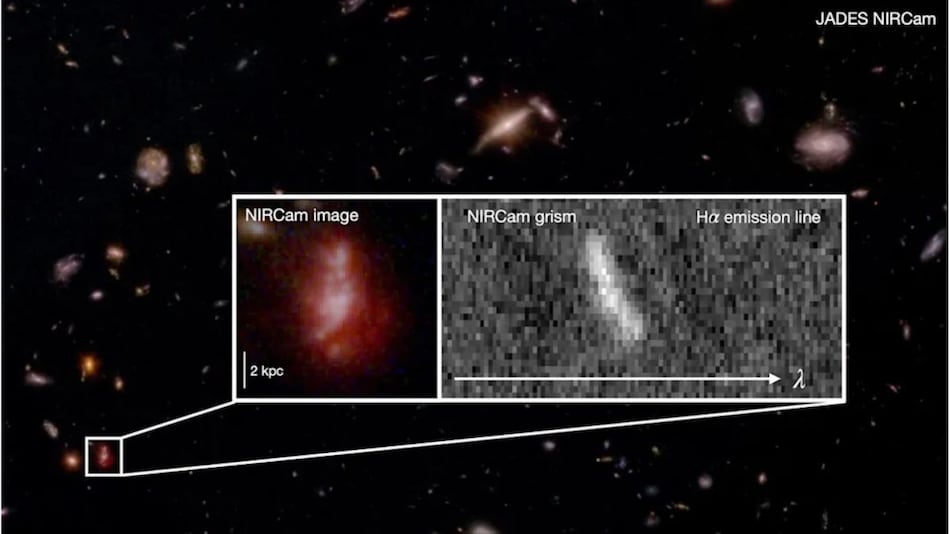

Photo Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, B. Robertson
JWST reveals early galaxies were chaotic clouds that evolved into stable disks
According to new findings by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the first galaxies were much more messy compared to the ones we have today. An analysis of more than 250 systems by researchers at the University of Cambridge, 0.8-1.5 billion years after the Big Bang, revealed the majority of them to be turbulent, clumpy - not the smooth rotating discs of the present day galaxies. During this era, turbulence is caused by the gravitational action and creation of stars, and thus, galaxies found it difficult to settle. The results indicate that these galaxies became cooler over time.
Chaotic Early Galaxies
In the study, JWST's infrared cameras traced the motion of ionised hydrogen gas. Almost all the galaxies appeared "still chaotic, with gas puffed up and moving in all directions", as lead author Dr Lola Danhaive notes. Only a few show signs of settling into smooth rotation. Earlier surveys had spotted a few well-ordered disks, but by examining hundreds of smaller galaxies the team finds that most early systems grew via "frequent mergers and bursts of star formation".
From Chaos to Calm
As star formation slowed and gas reservoirs were used up, galaxies gradually stabilised. The data span the epoch of reionisation through to the later "cosmic noon" of peak star formation, demonstrating how galaxies evolved "from chaotic clumps into ordered structures". Danhaive notes that early on strong starbursts "disrupt the ordered motions" of a galaxy's gas, whereas later on "galaxies grow their mass and become more stable". In other words, the infant galaxies eventually matured into the graceful spiral galaxies we see today.
Get your daily dose of tech news, reviews, and insights, in under 80 characters on Gadgets 360 Turbo. Connect with fellow tech lovers on our Forum. Follow us on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News for instant updates. Catch all the action on our YouTube channel.
Related Stories
- Samsung Galaxy Unpacked 2026
- iPhone 17 Pro Max
- ChatGPT
- iOS 26
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Apple Vision Pro
- Oneplus 12
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- iPhone 13
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Realme V30
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- iQoo 12
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Giottus
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- JioGlass
- HD Ready TV
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
- Vivo Y51 Pro 5G
- Itel Zeno 100
- Poco C85x 5G
- Realme Note 80
- Vivo V70 FE
- Realme C83 5G
- Nothing Phone 4a Pro
- Infinix Note 60 Ultra
- MacBook Neo
- MacBook Pro 16-Inch (M5 Max, 2026)
- Tecno Megapad 2
- Apple iPad Air 13-Inch (2026) Wi-Fi + Cellular
- Tecno Watch GT 1S
- Huawei Watch GT Runner 2
- Xiaomi QLED TV X Pro 75
- Haier H5E Series
- Asus ROG Ally
- Nintendo Switch Lite
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAID5BN-INV)
- Haier 1.6 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (HSU19G-MZAIM5BN-INV)